Which Countries in the World Have Nuclear Weapons, and Which Are Suspected
More than seven decades have passed since the first explosions over Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the world is still in the nuclear age. The latest conflicts in the Middle East have once again raised questions about nuclear weapons and which countries possess them.
The conflict between Iran and Israel began on June 13 this year, when Israel launched surprise airstrikes on key Iranian nuclear and military facilities. Iran responded by launching ballistic missiles at Israeli cities. The United States joined the conflict on June 22 with airstrikes on three Iranian nuclear facilities. In retaliation, Iran launched missiles the next day at a U.S. military base in Qatar. A ceasefire was declared after 12 days of intense fighting.
One of the immediate causes of the attacks was Israel's claim that Iran had accelerated uranium enrichment and was nearing the capability to build a nuclear weapon – reports N1.
From the "Manhattan Project" to the Global Arms Race
It all began during World War II. The U.S., with help from its allies, developed the first nuclear weapon through the Manhattan Project. The bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki marked the beginning of the nuclear age.
After the war, the Soviet Union detonated its first atomic bomb in 1949, starting the Cold War and an accelerated arms race. France, the United Kingdom, and China followed with their own nuclear programs. In an effort to curb further proliferation, the U.S. and other nations negotiated the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) in 1968 and the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) in 1996. These became the foundation for recognizing nuclear powers under the NPT framework.
Arms Control
At the time the NPT was signed, the nuclear stockpiles of the U.S. and the Soviet Union numbered in the tens of thousands. Starting in the 1970s, American and Soviet leaders negotiated a series of bilateral arms control agreements that helped limit and later reduce the size of nuclear arsenals.
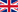
Which Countries Possess Nuclear Weapons Today?
Today, nine countries possess nuclear weapons: the U.S., Russia, China, France, the United Kingdom, India, Pakistan, North Korea, and Israel. Some countries are also suspected of secretly developing nuclear capabilities.
Countries with nuclear weapons fall into two categories: those recognized as nuclear-armed under the NPT, and those that possess nuclear weapons but are not NPT signatories.
The following five countries are permanent members of the UN Security Council and recognized as "nuclear weapon states" under the NPT:
Russia
About 5,580 warheads, with powerful ICBM systems (Yars, Sarmat), SLBM Bulava, and a large number of tactical warheads.
United States (USA)
About 5,200 warheads, including strategic intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM Minuteman III), submarine-launched ballistic missiles (Trident II), and B61 nuclear bomb aircraft.
China
Estimated at around 500 warheads, rapidly expanding its arsenal with new ICBM DF-41 and JL-3 submarine systems.
France
About 290 warheads, mostly deployed on submarines (M51 SLBM) and strategic aircraft with ASMP-A missiles.
United Kingdom
About 225 warheads, deployed exclusively on Vanguard-class submarines with Trident II missiles.
Some countries have developed nuclear weapons outside the NPT and do not officially acknowledge possessing them:
India and Pakistan – around 170 warheads each, with regionally focused ballistic and tactical systems (Agni, Shaheen, Babur).
North Korea – estimated up to 50 warheads, with new ICBMs Hwasong-17 and Hwasong-18.
Israel – a country that has never officially acknowledged possessing nuclear weapons but is estimated to have around 90 warheads, with Jericho III missiles and nuclear-capable submarines.
Countries suspected of pursuing nuclear weapons programs or possessing the capability to develop them covertly include Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Syria.
Countries that have voluntarily given up their nuclear arsenals include South Africa, Belarus, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan.
Why Do Countries Still Seek Nuclear Weapons?
Nuclear weapons remain the ultimate guarantee of security for many regimes.
As the world enters a new phase of global insecurity and rising international tensions, the issue of nuclear arms remains one of humanity's greatest challenges.