Which Activity Is Healthier – Running or Walking?
Walking and running provide numerous health benefits. The best option for you depends on your health goals, mobility, and personal preferences.
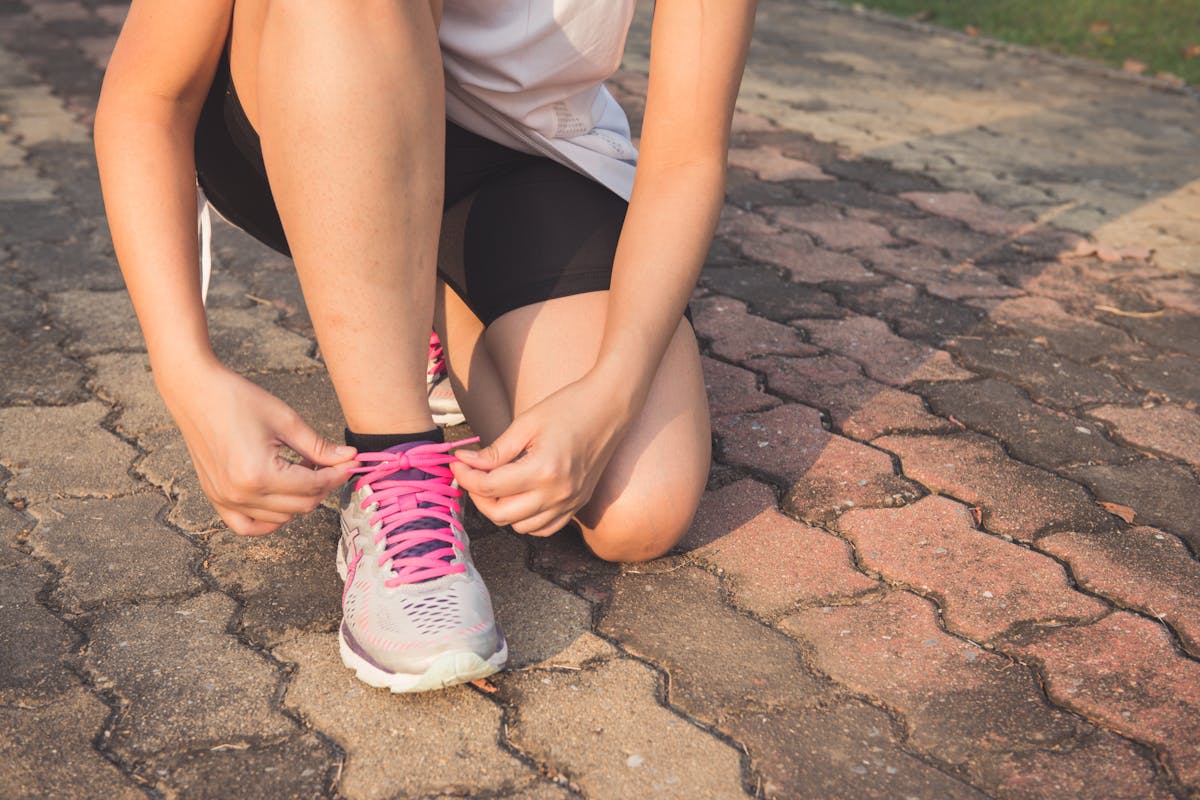
Walking and running are excellent forms of cardiovascular exercise. Neither is necessarily “better” than the other. The best choice for you depends on your fitness and health goals, reports N1.
If you want to burn more calories or lose weight quickly, running is the better choice. However, walking also offers numerous health benefits, including helping maintain a healthy body weight, according to Healthline.
Keep reading to learn more about the benefits, risks, and types of walking and running that suit your health goals.
Benefits of Cardio Exercise
Walking and running are aerobic cardiovascular, or cardio, exercises. According to researchers, some of the health benefits of cardio exercises include:
helping with weight loss or maintaining a healthy body weight,
boosting immunity,
helping prevent or manage chronic diseases,
strengthening the heart,
potentially extending lifespan.
Cardiovascular exercises are also good for mental health.
One study found that both running and walking can reduce anxiety and depression. They can also improve mood and self-confidence.
Another study found that just 10 minutes of moderate-intensity running improved participants’ moods after exercise. So, you don’t need to run for hours to enjoy these benefits.
Is Walking Better Than Running?
Walking can provide many of the same benefits as running. One study showed that running burns roughly twice as many calories as walking.
It takes about 3,500 calories to lose one kilogram. If your goal is weight loss, running is a better choice than walking.
If you’re new to exercise or can’t run, walking can still help you get in shape. Walking is accessible to almost all fitness levels. It can strengthen your heart and boost your energy levels.
Walking vs. Running for Weight Loss
Brisk Walking and “Power Walking” vs. Running
Brisk walking means walking at a fast pace, usually 4.8 km/h or faster, which raises your heart rate. You can burn more calories per minute brisk walking than at a normal pace, according to Healthline.
Power walking usually ranges from 4.8 km/h to 8 km/h, with some people walking at 11 to 16 km/h. Power walking burns a similar number of calories as running. For example, walking at 7.2 km/h for one hour burns the same calories as jogging at the same speed for one hour.
For an effective workout, try tempo training: speed up for two minutes, then slow down.
Brisk walking doesn’t burn calories as quickly as running. To burn the same number of calories as running, you’d need to walk longer. Still, it can be an effective workout for raising your heart rate, improving mood, and boosting aerobic fitness.
Walking with a Weighted Vest
Walking with a weighted vest can increase the number of calories burned. For safety, the vest should not be heavier than five to 10 percent of your body weight.
If you’re looking for an alternative way to lose weight or tone muscles, try interval walking: speed up for a set period, then slow down. Or, walk with light dumbbells in each hand.
Walking Uphill vs. Running
Walking uphill can burn a similar number of calories as running. If you maintain the same pace as on flat ground, you’ll burn more calories on an incline.
Look for a hilly area or use a treadmill with an incline. Increase the incline to five, 10, or 15 percent in intervals. If you’re a beginner, start gradually and work up to a 15 percent incline.
Benefits and Risks
Running is a great way to get fit and lose weight, but it’s also a high-intensity exercise. High-intensity exercises can put more stress on the body than low-intensity exercises, such as walking.
According to scientists, long-term running can lead to common injuries such as:
stress fractures
plantar fasciitis
ITB friction syndrome
Estimates suggest that 50 percent of runners experience an injury each year that prevents them from running.
If you’re a runner, you can take steps to avoid injury: don’t increase your mileage too quickly, and try incorporating other forms of training several times a week.
Or, instead, try walking. Walking offers many of the same health benefits as running, but without the same risk of injury.
Conclusion on Running and Walking
Both walking and running are excellent forms of cardiovascular exercise. At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week is recommended for maintaining health.
Walking is a smart choice if you’re a beginner and want to get in shape. If you want to lose weight or burn calories more quickly, try running.
If you’re new to running, start with a program that alternates walking and running.
Always consult your doctor before starting a new exercise routine.