Do You Have Elevated Cortisol? Symptoms That May Indicate This Problem
In recent years, cortisol has increasingly been mentioned as the cause of numerous issues – from chronic fatigue and insomnia to the accumulation of fat tissue. Although it often has a negative connotation, this hormone plays a key role in the normal functioning of the body.
“Cortisol regulates the body's response to stress, blood sugar levels, metabolism, inflammatory processes, and even the sleep-wake cycle,” explains Dr. Erika Armstrong for Eating Well.
What Is Cortisol and Why Is It Important?
Cortisol is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands, and its levels naturally vary throughout the day – it is highest about 30 minutes after waking up and lowest at night. In stressful situations, cortisol levels rise rapidly to help the body react quickly – heart rate increases, blood sugar levels rise, and the body prepares for “fight or flight.”
The problem arises when cortisol remains constantly elevated, even without a real physical threat. Chronically elevated cortisol levels can seriously damage your health. According to Eating Well, it increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and other inflammatory conditions.
According to Dr. Armstrong, the only sure way to know if you have high cortisol is through laboratory testing. However, there are symptoms that may indicate a problem, reports Sombor.info.
Most Common Symptoms of Elevated Cortisol
-
Sleep Problems
If you have trouble falling asleep or wake up in the middle of the night, cortisol might be the cause. “Cortisol should be low at night, but stress or a drop in blood sugar can increase it and wake you up,” says Armstrong. Research shows that higher cortisol levels in the evening worsen sleep quality.
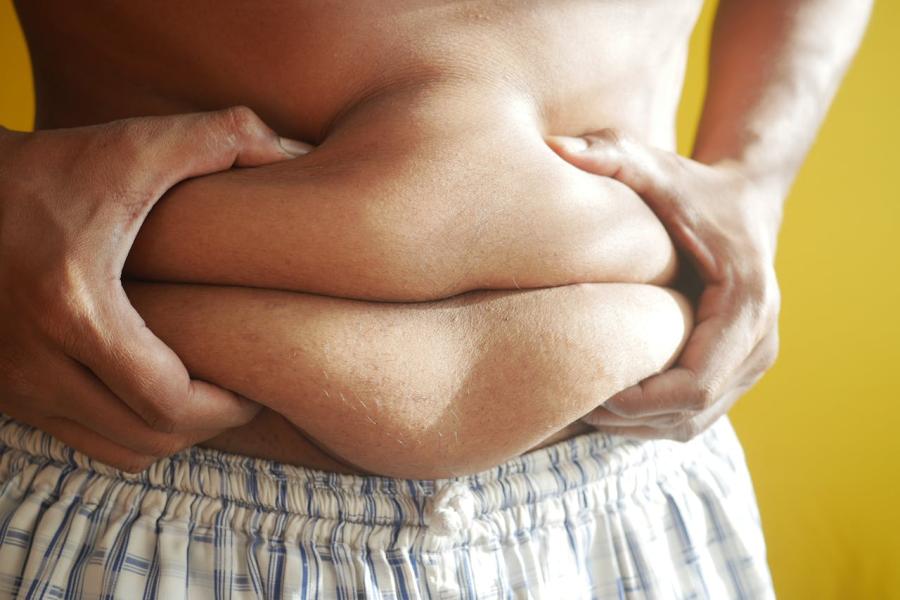
2. Fat Accumulation Around the Abdomen
If you notice you're gaining weight in the abdominal area without changes in your diet or physical activity, a hormonal imbalance might be the cause. “Cortisol promotes fat storage around the stomach as a form of protection,” says the doctor.
3. Fatigue and Irritability
When cortisol is chronically high, you may feel mentally tense even when physically exhausted. “Cortisol can keep us alert while we feel completely drained,” Armstrong explains. In the long term, this condition can impair memory, concentration, and other cognitive functions.
How to Naturally Lower Cortisol and Reduce Inflammation?
Reducing cortisol helps regulate inflammation and lowers the risk of chronic diseases. Here are some scientifically proven tips:
Anti-inflammatory diet: Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, a variety of fruits and vegetables, and dietary fiber.
Blood sugar stabilization: Eat regular meals with protein, healthy fats, and fiber – this prevents cortisol spikes.
Stress management: Meditation, mindfulness techniques, and regular rest help reduce stress.
Healthy sleep: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and relaxing bedtime routines.
Gut health: A balanced gut microbiome boosts immunity and reduces inflammation.