The Shroud of Turin is shrouded in mystery. For centuries it has been considered a holy relic, but according to yet another study, this Christian artifact is not what it seems.
The old linen cloth and its faint imprint of a man's facial contours, resembling traditional depictions of Jesus, was first documented in France in 1354. To this day, no one knows who the imprint actually depicts or how it was created.
Some Christians believe it is the very shroud that covered the body of Jesus Christ after his death (although the Catholic Church neither endorses nor rejects this idea). Skeptics consider it either a work of art or a forgery – reports Sombor.info.
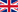
Although the disputed relic bears a faint imprint of a naked adult man with long hair and a beard, Brazilian 3D designer and researcher Sisero Moraz claims that the imprint on the shroud was not made from a real man but from a sculpture.
A new analysis, published in the journal Archaeometry, supports a hypothesis first proposed in 1978 that the image on the shroud is a work of art.
According to this hypothesis, the image most likely emerged by laying the cloth over a low relief – a sculpture slightly raised from the background – and then the linen was rubbed with pigment or darkened in some way.
Moraz is a self-taught expert in historical facial reconstruction, meaning he is skilled at comparing two-dimensional and three-dimensional images. When he first looked at the rigid and straight forms of the body on the shroud, they didn’t seem to match real human anatomy. The fabric distortion didn’t appear as if it had been wrapped around an actual human body.
Instead, Moraz thought it might be an image on fabric or a low-relief imprint.
To test this idea, he created reconstructions of both possibilities.
The Brazilian used a computer model to compare how cloth looks when wrapped around a human body model versus when laid over a low-relief sculpture.
In the case of the three-dimensional model representing an authentic human body, the figure's imprint appeared wider and more stretched than on the Shroud of Turin when the cloth was spread out.
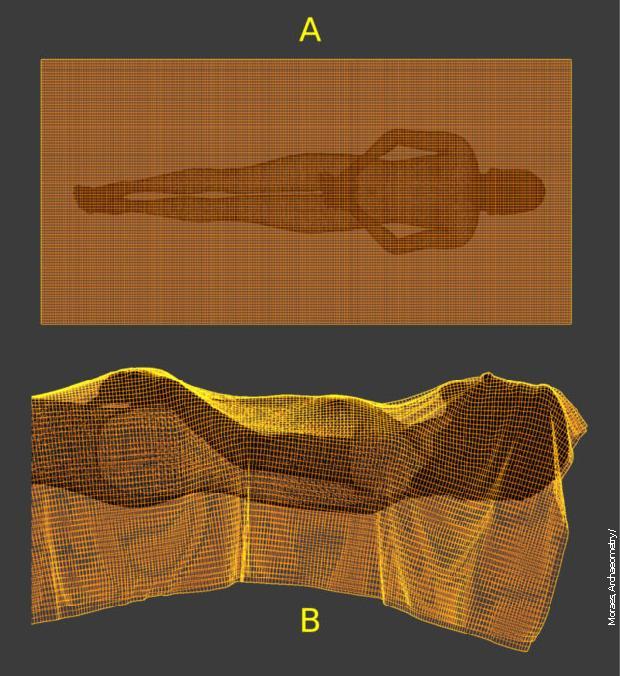
A) Top view with fabric mesh placed over the body. B) Side view of the simulation of fabric lying over the body
This phenomenon is known as the "Agamemnon mask effect," named after the golden funerary mask from ancient Greece that was first molded to a face and then flattened. This caused the facial features to become slightly distorted.
"The printed image, created from the contact zones of the low relief, shows high conformity with the one on the Shroud of Turin, significantly matching its contours, even considering that the base is not completely flat," concludes Moraz.
His analysis of the shroud provides evidence that it is not an imprint of any body (let alone that of Jesus Christ), while avoiding the recent academic debate over the artifact's age.
Some attempts at dating using radiocarbon methods suggest the shroud originated in the Middle Ages, but one recently published controversial study dates it closer to the first century AD.
Like Moraz, other researchers have noted that the shroud is not structurally deformed in a way that would be expected if it had been in contact with a real body. However, the details are very faint, and academic debates about how exactly the imprint was made continue.
"Using the described free open-source tools, anyone with the necessary skills can recreate the simulations of fabric dynamics and contact mapping, testing the presented scenarios," says Moraz.
This work, he concludes, "highlights the potential of digital technologies to answer or unravel historical mysteries, merging science, art, and technology in a collective and reflective search for answers."